Submitted by: Suha Abu Khalaf, MD
Institution: University of Missouri Health Care
Email: Suhaabukhalaf@hotmail.com
Date: 3/31/2021
History
A 63-year-old male who was transferred from an outside Hospital for acute hypoxic respiratory failure secondary to COVID-19 initially to the regular hospital floor service then later to the medical intensive care unit (MICU) within 24 hours of arrival. For 10 days prior to admission the patient has been experiencing generalized body aches, subjective intermittent fever with associated cough and progressively worsening shortness of breath.
Shortly after admission was transferred to the MICU due to increasing respiratory requirements, 2L to 10L/min within hours, and ultimately intubation.
Chief Complaint:
Shortness of breath
Medical Hx
Diabetes on insulin
Hypertension
Gout
Family Hx
Denies family history of cancer, heart disease
Surgical Hx
No surgical history
Social hx:
Denies smoking cigarettes, drinking alcohol, drug abuse
Review of Symptoms:
Present
Stated that he has been experiencing cough with whitish productive sputum, associated with significant shortness of breath, chest tightness, chest pain. Patient has also been endorsing multiple bouts of diarrhea over the last couple of days
MEDICATIONS – at admission
allopurinol, 300 mg, Oral, Daily
rosiglitazone, 4 mg, Oral, bid
colchicine, 0.6 mg, Oral, tid, PRN
indomethacin, 50 mg, Oral, tid
insulin glargine, 30 units, Subcutaneous, Daily
lisinopril, 40 mg, Oral, Daily
metformin, 1000 mg, Oral, bid
metoprolol, 25 mg, Oral, bid
acetaminophen Extra Strength, 1000 mg, Oral, tid, PRN
Physical Examination:
T: 36.4 °C HR: 92 bpm RR: 42 breaths/minute BP: 148/69 mmHg SpO2: 92%
Gen: AO x3, tachypneic, in moderate respiratory distress
HEENT: MM dry, EMOI, PERRLA
Neck: Supple, No LAD
CVS: S1,S2 positive
Lungs: Decreased air entry at lung base, tachypneic, moderate respiratory distress
Abd: Soft, no organomegaly, bowel sounds positive
Neuro: Patient alert, oriented, power 5/5 in all extremities, 2-12 cranial nerves normal bilaterally, sensation is intact, no cerebellar signs
Extremities: Warm and dry, no edema
Admission Labs:
CHEMISTRY/METABOLIC PANEL
Na – 141 mmol/L
K – 4.2 mmol/L
Cl – 110 mmol/L
HCO3 – 16 mmol/L
BUN – 58.6 mg/dl
Creatinine – 2.17 mg/dl
Glucose – 116 mg/dl
Ca – 7.6 mg/dl
Total Protein –4.9 gm/dl
Albumin – 2.7 gm/dl
Total Bilirubin – 0.8 mg/dl
AST – 73 units/L
ALT – 35 units/L
ALP – 94 units/L
CBC
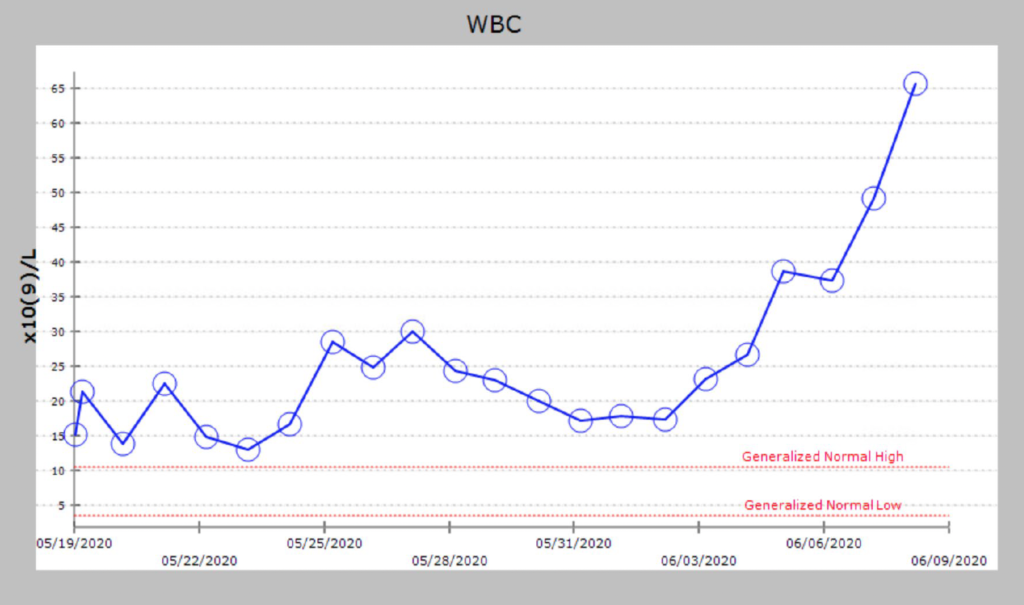
WBC – 15 x 103 /cmm
Hb – 13 gm/dl
Platelets – 307 x 103 /cmm
%PMNLs – 93 %Lymphocytes – 3 % Eosinophils – 0
Other labs
ABG: pH: 7.42; pCO2: 25.9; pO2: 58.2; FiO2: 89%
troponin – <0.01
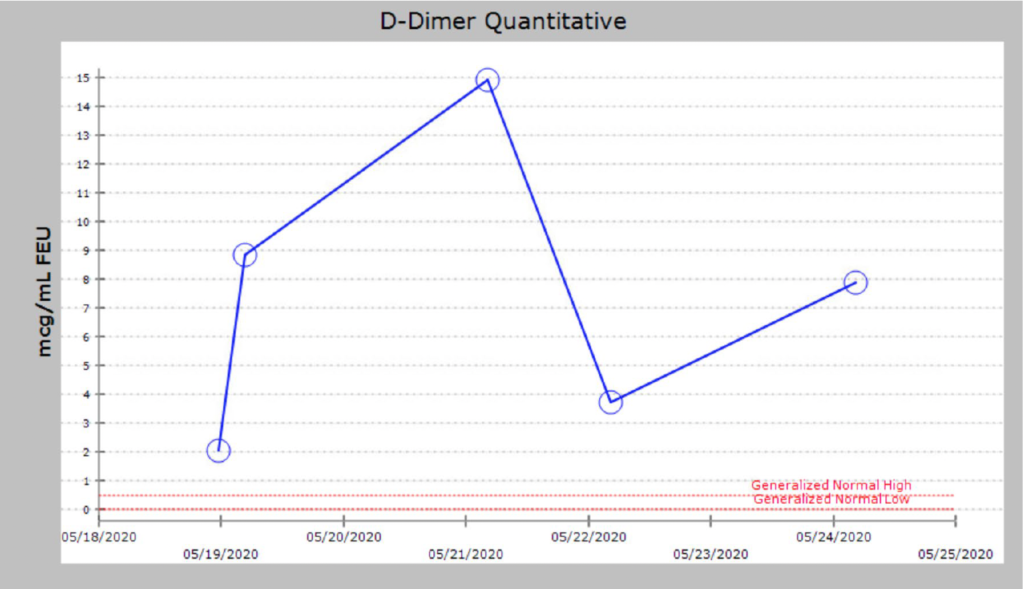
d-dimer 1290 (reference range 0-400)
Viral Respiratory Panel – Negative MRSA
Nasopharyngeal Screen – Negative
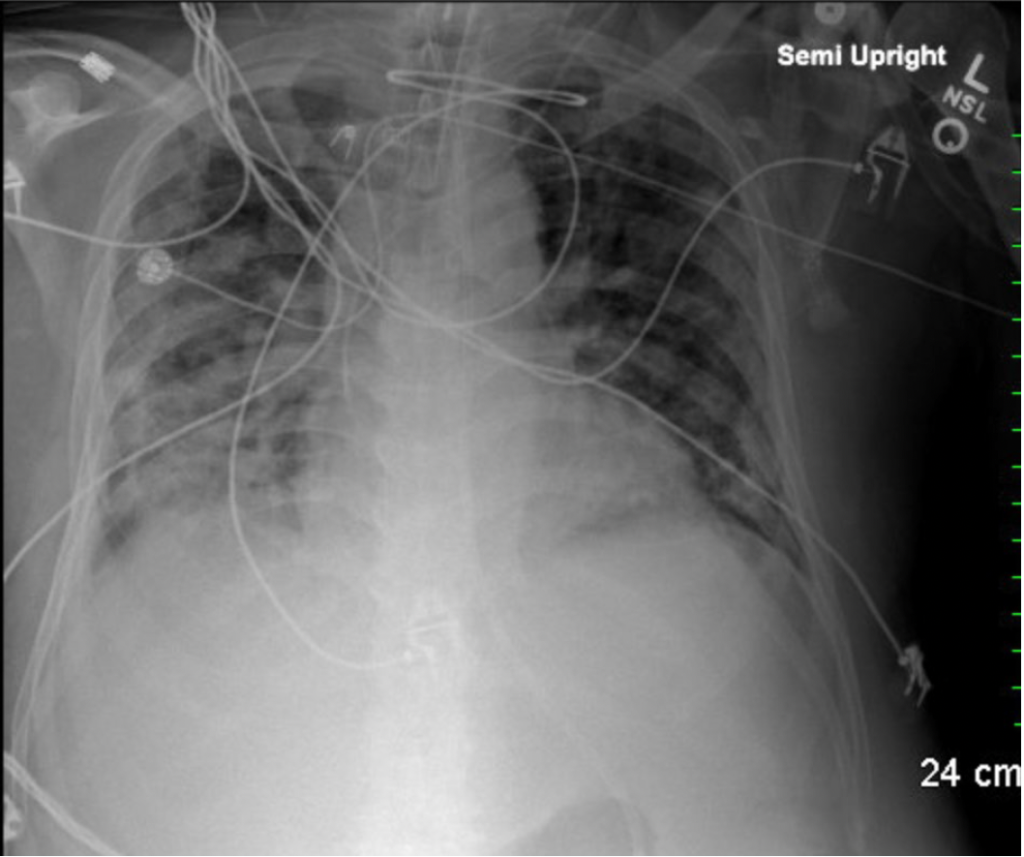
CXR: Chest x-ray: Bilateral diffuse lung opacities consistent with atypical viral pneumonia
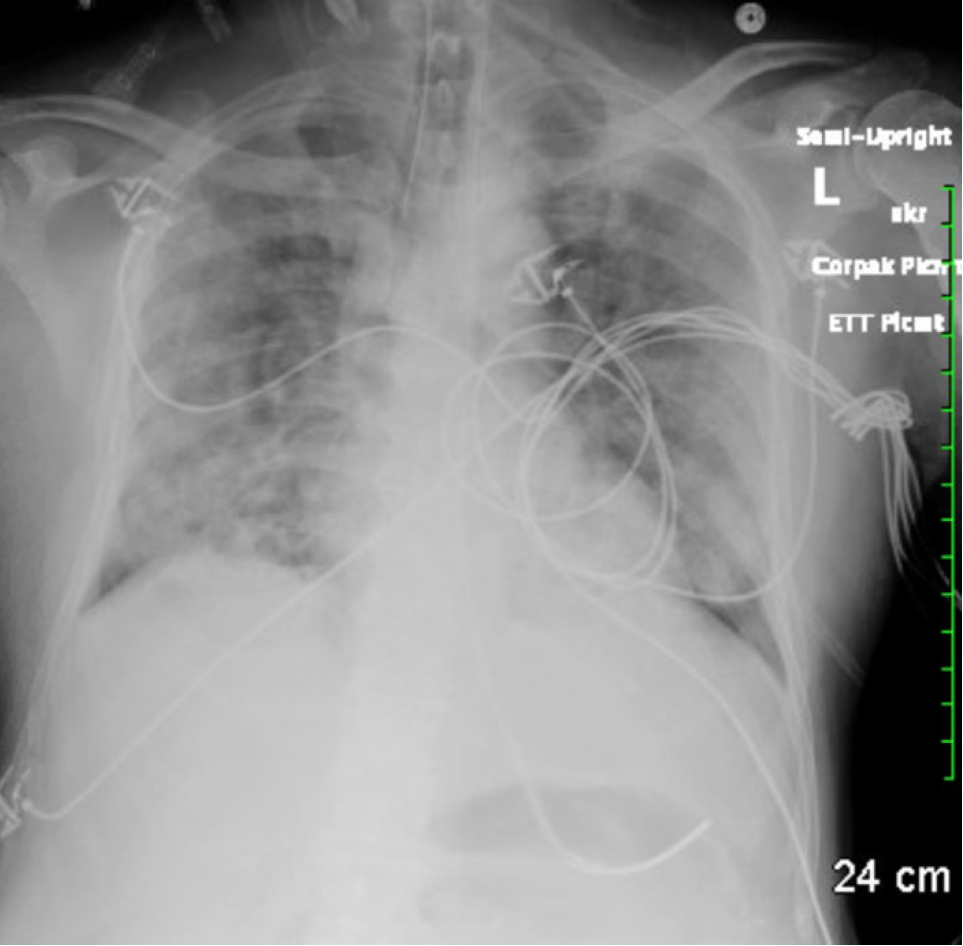
Timeline of Hospital Course / Images:
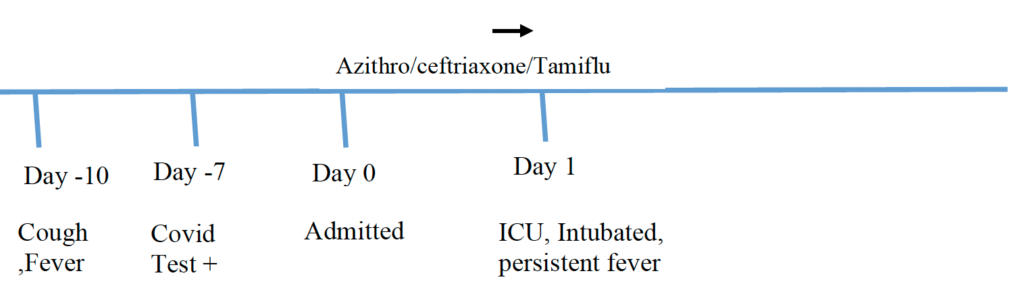
Day 1: Sputum Cultures, imaging Endotracheal intubation, Respiratory pathogen panel were obtained. transferred to MICU. Remdesivir treatment which patient was started on. He also received convalescent plasma as well. Was started on ceftriaxone, azithromycin and oseltamavir.
Day 2: febrile up to 38.9 Celsius and also tachycardic into the 130s. Norepinephrine had been increased up to 8 mics an hour as well. Patient maintained his urine output of 30 to 40 cc/h but had no BM overnight. Morning ABG showed a worsening PF ratio. Was paralyzed and proned.
Day 3: ceftriaxone, azithromycin and Tamiflu were discontinued since RPP and pneumonia PCR were negative. was started on insulin drip for hyperglycemia. He also had his bicarb drip advanced to 3 Amps per bag and rate increased to 125 cc an hour. He also had 4 episodes of liquid stools and a rectal tube was inserted. He remains on Levophed and is at 14 mics as of this morning. Vitals wise he has been afebrile, but heart rate has been mildly tachycardic
Day 4: has been off of all pressors. He continues to have excellent urine output and has been afebrile.
Day 5: was on pressure support at the beginning then became hypoxic and required return to volume control mode. Patient also had hypotension was restarted on vasoactive drugs. Patient also was febrile up to 38.4 C.
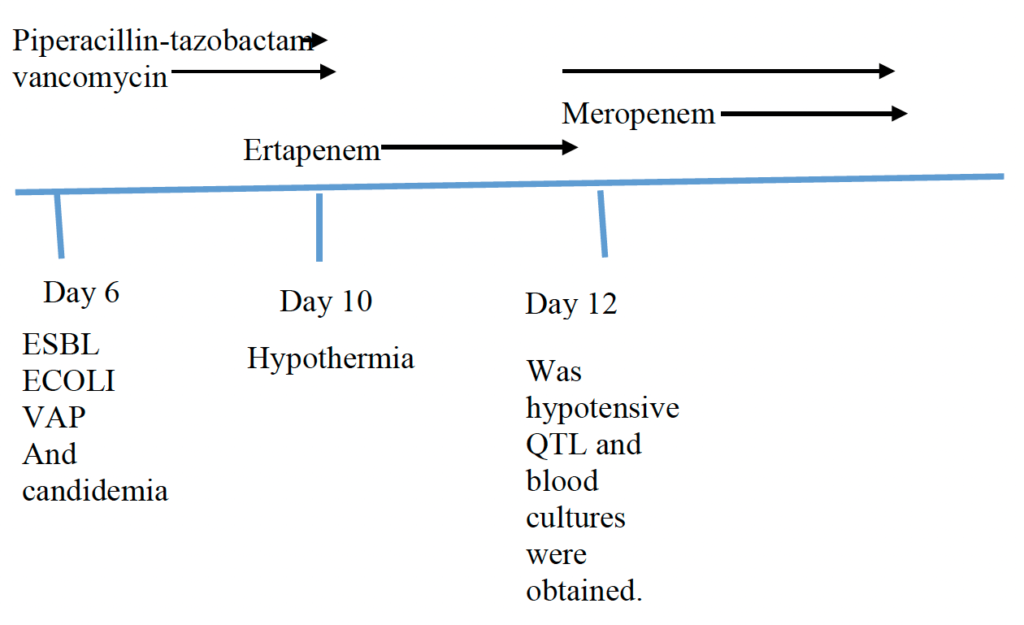
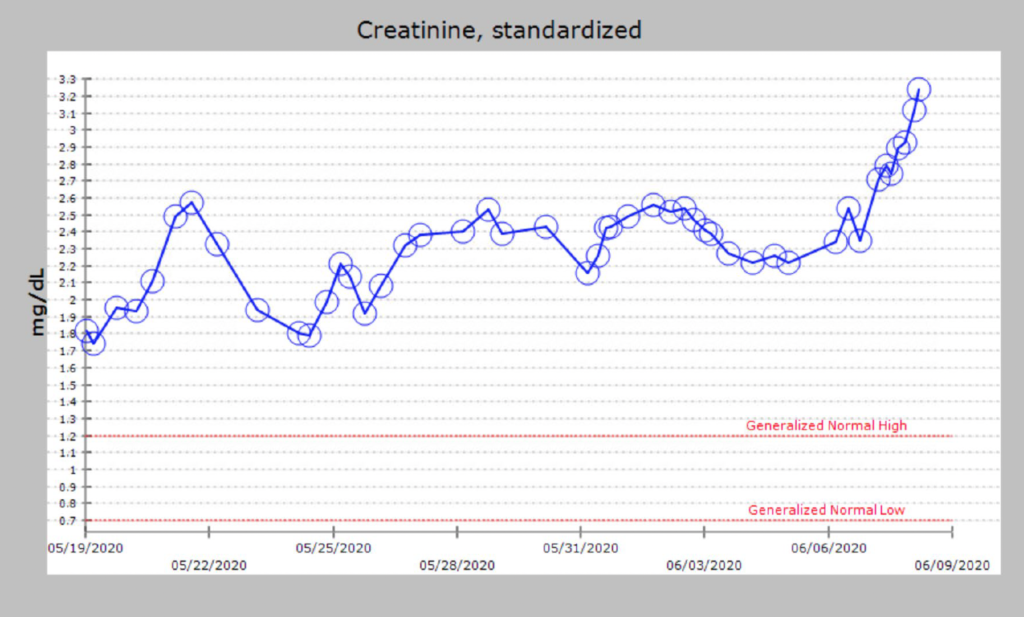
Day 6: developed AKI and hyperkalemia. leukocytosis worsening 28. QTL and blood cultures were obtained. Was started on vancomycin and piperacillin-tazobactam.
Day 7: has been febrile with a T-max of 38.5. He continues on norepinephrine currently at 8 and vasopressin
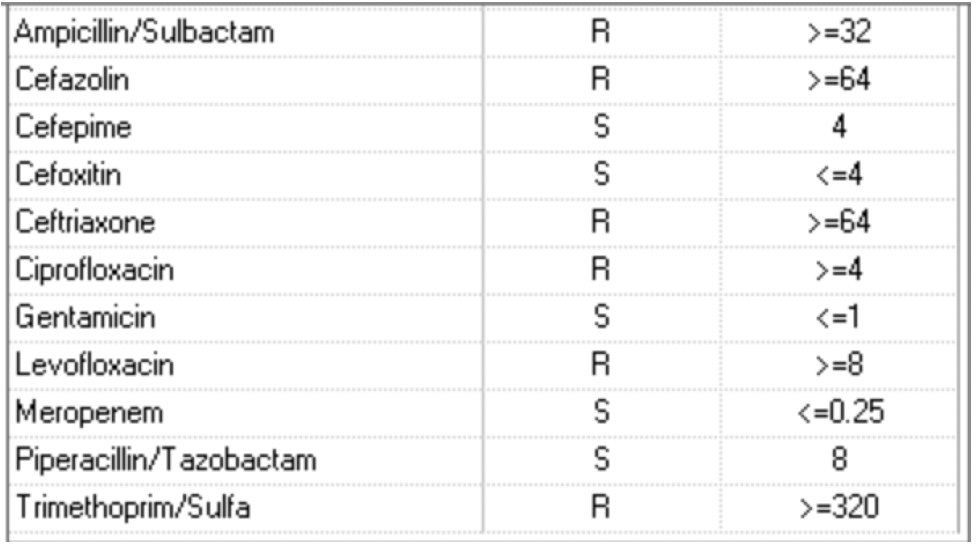
Day 8: FIO2 needs worsening to 75%. Day QTL culture grew >10,000 CFU/ml Escherichia coli.
Day 9: vancomycin and piperacillin/tazobactam were discontinued. QTL culture Confirmatory test indicates Escherichia coli.
ESBL producer. Was switched to Ertapenem.
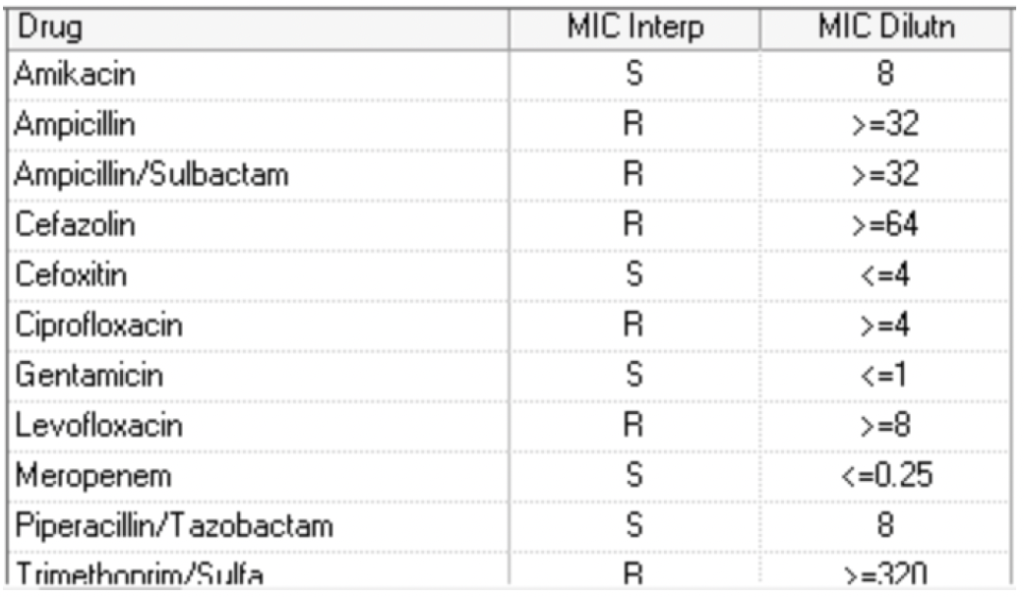
Day 10: He also has continued to require norepinephrine and vasopressin for inotropic support. He also has been having liquid stools with about 1400 cc of output over the past 24 hours. He also had some mild hypothermia at 35.9 C.
Day 11: patient had sinus tachycardia throughout the night. He remains on norepinephrine and vasopressin.
Day 12: He was hypotensive. Vancomycin was restarted. Ertapenem was switched to meropenem. Peripheral and central Blood and QTL cultures were obtained. CXR was Grossly unchanged bilateral multifocal airspace opacities.
Day 13: Patient was having persistent fevers and increasing hypotension despite what appear to be appropriate antibiotic coverage. He became very tachypneic with respiratory rates in the 30s to 40s. CT head, chest, abd/pelvis to eval for occult infection but none were done as patient’s oxygenation status wasn’t stable enough to tolerate going to CT scans. BL LE and UE venous duplex to eval for DVT as a cause for fever showed DVT in LLE and RUE for which Heparin gtt was started.. ACS consulted for Tracheostomy.
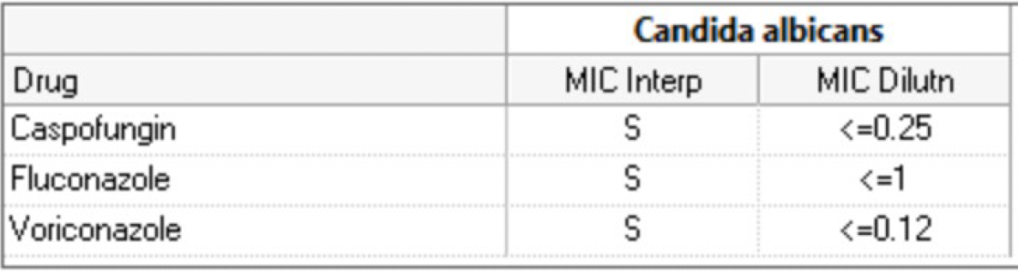
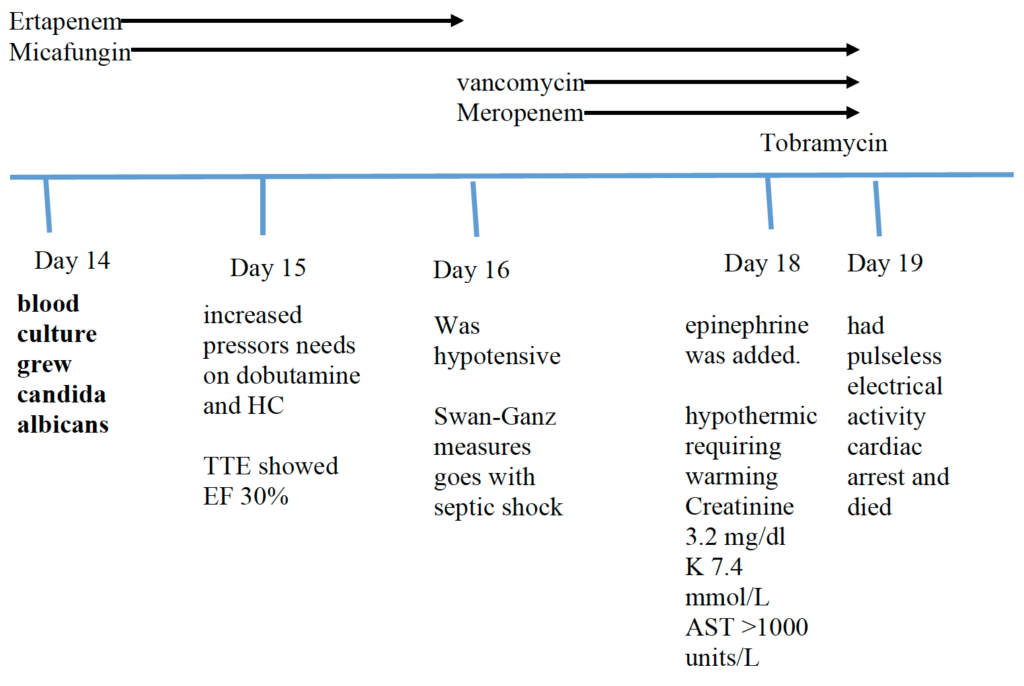
Day 14: central blood culture grew Candida albicans for which Micafungin was started. Central line was removed and another line was inserted in different location.
QTL grew E coli: >10,000 CFU/ml Escherichia coli – Confirmatory test indicates ESBL producer.
Day 15: continued to worsen clinically with increased pressors needs. Transthoracic echo showed new ejection fraction of 30%. Was started on Dobutamine and hydrocortisone.
Day 16-18: patient continued to decline. He had a Swan-Ganz catheter inserted overnight which revealed a cardiac index of 2.7 and cardiac output of 5.8. His systemic vascular resistance was around 690. He became more hypotensive and required addition of fourth inotrope. He has also been hypothermic and requiring warming likely due to sepsis. Continued on vancomycin and micafungin, was switched to meropenem. also giving 1x dose of tobramycin for septic shock from likely another occult infectious process
Day 19: had pulseless electrical activity cardiac arrest and died.
CXR on day 6:
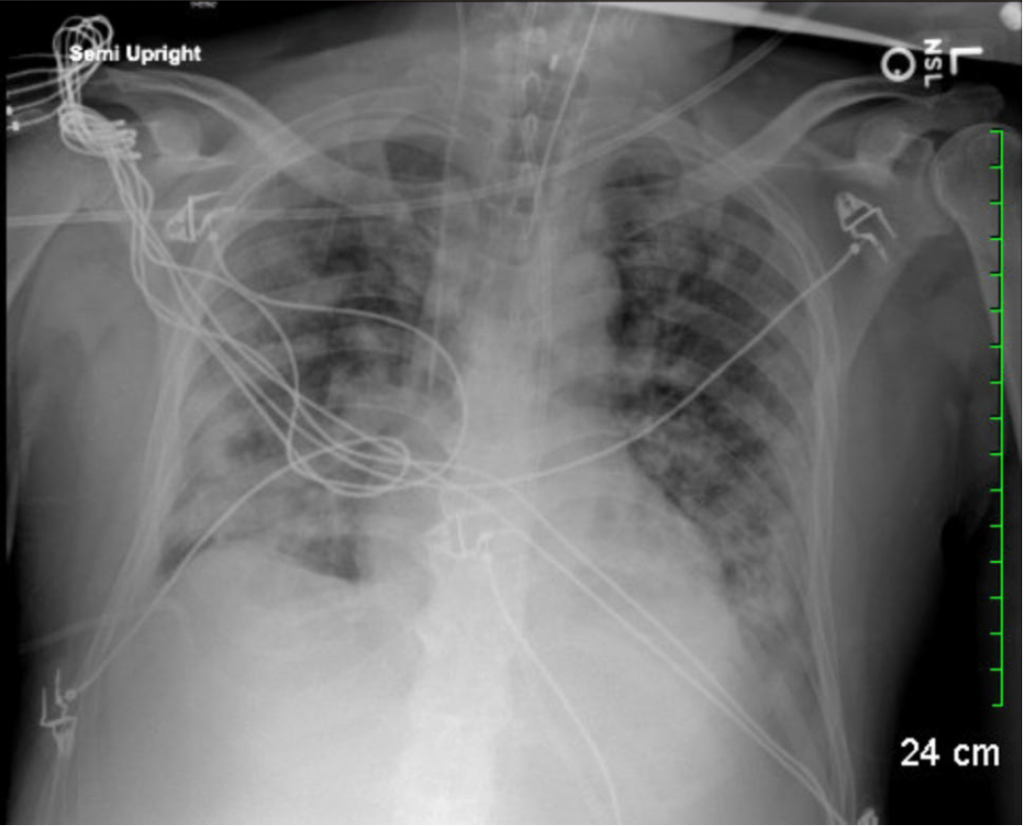
CXR on day 12:
WHAT DID YOU FIND MOST CHALLENGING ABOUT THIS CASE?
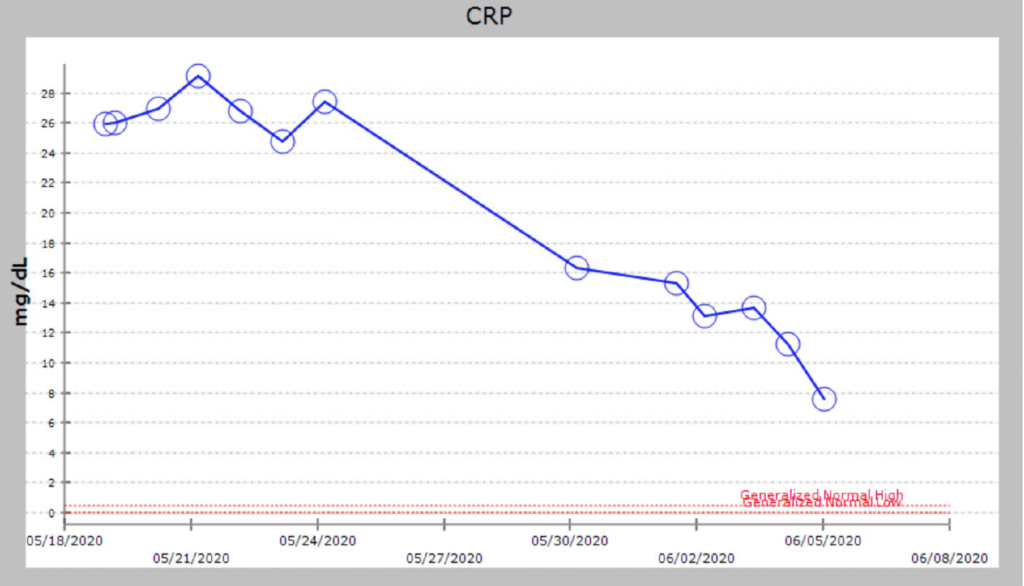
Finding the source of infection that could explain the candidemia, progressive worsening leukocytosis and refractory septic shock.
Patient was so sick like many other COVID patients, so difficult to obtain appropriate evaluation.
WHAT DO YOU SEE AS THE BIGGEST UNMET EDUCATIONAL NEED IN MANAGING COVID-19-ASSOCIATED INVASIVE FUNGAL INFECTIONS?
Realizing when to consider fungal infection as an etiology of persistent hypoxemia.
Go here for continuing education activity / case discussion.
