(Bainer) Subramaniam (1971)<
Macroscopic morphology
Colonies on potato dextrose agar at 25°C are initially white, soon becoming dark gray to an olivaceous black with a black reverse. Rapid growth. Texture is woolly to cottony.
Microscopic morphology
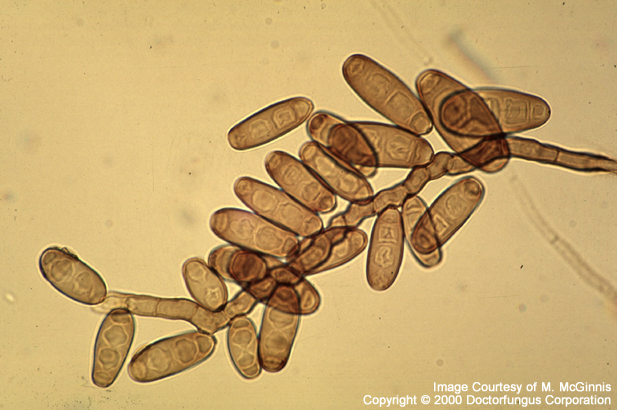
Hyphae are septate and dark. Conidiophores may be up to 300 µm in length, are sympodial, geniculate, simple or branched, bearing conidia through pores or openings (poroconidia). Conidia contain predominately 3 transverse distosepta or pseudosepta (septa that do not extend to the cell wall with cells enclosed within sacs) and 4 cells. They measure approximately 20-40 x 9-14 µm. A flattened hilum or point of attachment is seen on the basal cell. Conidia germinate from both poles (bipolar).
Special notes
One of several “graminicolous” species common on plant material, particularly grasses. This is the most common Bipolaris species cited in causing human disease and a frequent cause of phaeohyphomycosis [1487]. It is also often implicated as a cause of fungal sinusitis [352], particularly in the Southern and Southwestern U.S., and other temperate areas. It has been reported as an agent of cutaneous disease [2177], mycotic keratitis [1021], and allergic fungal sinusitis [2214]. Systemic disease includes a dual mycosis with Torulopsis glabrata in a dog [2387], a fatal endarteritis following aortic valve replacement [1680], fungal peritonitis [204], meningitis [1300], and disseminated disease in a neonate [1570].
FTL* in vitro susceptibility data
| AMB | CAS | ITRA | VORI | FLU | POSA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.125 µg/ml=3 | 0.25 µg/ml=5 | 0.06 µg/ml=3 | 0.5 µg/ml=4 | 16 µg/ml=1 | 0.06 µg/ml=2 |
| 0.25 µg/ml=8 | 0.125 µg/ml=3 | 1.0 µg/ml=6 | 64 µg/ml=6 | ||
| 0.5 µg/ml=1 | 0.25 µg/ml=3 |
| Drug/N | AMB/12 | CAS/2 | ITRA/9 | VORI/10 | POSA/2 | FLU/7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIC Range | 0.125-0.5 | 0.25 | 0.06-0.25 | 0.5-1.0 | 0.06 | 16-64 |
| MIC50 | 0.25 | ** | 0.125 | 1.0 | ** | ** |
| MIC90 | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
* Fungus Testing Laboratory unpublished data (CLSI M38-A)