Synonyms
Chromomycosis
Definition
Chromoblastomycosis is a chronic localized infection of the skin and subcutaneous tissue that follows the traumatic implantation of the etiologic agent. The lesions are verrucoid, ulcerated, and crusted, and may be flat or raised 1-3 cm. Satellite lesions may develop following autoinoculation and by lymphatic spread to adjacent areas. The mycosis usually remains localized with extensive keloid formation. After many years, the lesions may resemble the head of a cauliflower [1485]. Many different fungi cause this disease. The disease takes its common name from the fact that most of the etiologic agents are dark-walled. Some of the causative agents (e.g., N/A(L):Fonsecaea pedrosoi and Phialophora verrucosa may disseminate to the brain [2093]. Elephantiasis and lymphatic stasis can occur as a result of secondary infections [692].
Forms of the disease
- cicatricial
- nodular
- plaque
- tumorous
- verrucous
Prognosis and therapy
The infection usually remains localized, but hematogenous dissemination in the immunosuppressed host has been rarely reported with a grave prognosis [1388]. Early stages of chromoblastomycosis are treated with surgical excision, electrodesiccation, cryosurgery or topical antifungals [1797]. Thiabendazole, 5-fluorocytosine, and amphotericin B have all been used topically. Advanced cases may require systemic treatment for long periods of time. Itraconazole and terbinafine are the drugs of choice [287, 692, 1857]. Results with fluconazole have been dissapointing [589]. In vitro data is promising for voriconazole [1492].
Histopathology
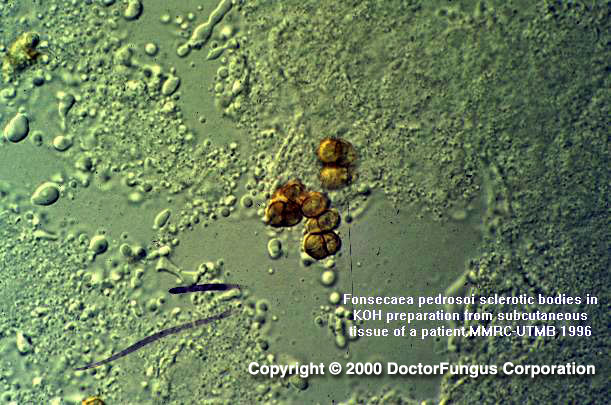
The skin lesions show a hyperkeratous pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia and keratolytic microabscesses in the epidermis. Dematiaceous hyphae and sclerotic bodies are found in the stratum corneum, with essentially only sclerotic bodies found in the areas of dermal inflammation. The sclerotic bodies are round, thick-walled, muriform, chestnut brown, and 5-12 µm in diameter. Brain abscesses are typically multilocular and well demarcated with thick walls. Irregular dematiaceous hyphae are seen in these abscesses.
Laboratory
Direct examination
Superficial crusts mounted in 10% KOH contain dematiaceous, septate branching hyphae 2-5 µm in diameter. Pus and granulation tissue obtained by curettage, or biopsy specimens of the epidermis and subcutaneous tissues typically contain dematiaceous round, thick-walled, muriform, bodies 5-12 µm in diameter.
Isolation
Inoculate the clinical specimens onto Sabouraud glucose agar and a medium containing cycloheximide, IMA or BHI agar with 10% sheep blood. Incubate at 30°C and discard negative cultures in 4 weeks.
Mycology (principal fungi)
- Cladophialophora carrionii
- N/A(L):Fonsecaea compacta
- N/A(L):Fonsecaea pedrosoi
- N/A(L):Phialophora verrucosa
Natural habitat
Soil and woody plant material